Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Quantum Institute for Light and Atoms, State Key Laboratory of Precision Spectroscopy, Department of Physics, School of Physics and Electronic Science, East China Normal University, Shanghai 200062, China
2 Shanghai Branch, Hefei National Laboratory, Shanghai 201315, China
3 School of Physics and Astronomy, and Tsung-Dao Lee Institute, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai 200240, China
4 Shanghai Research Center for Quantum Sciences, Shanghai 201315, China
5 Collaborative Innovation Center of Extreme Optics, Shanxi University, Taiyuan 030006, China
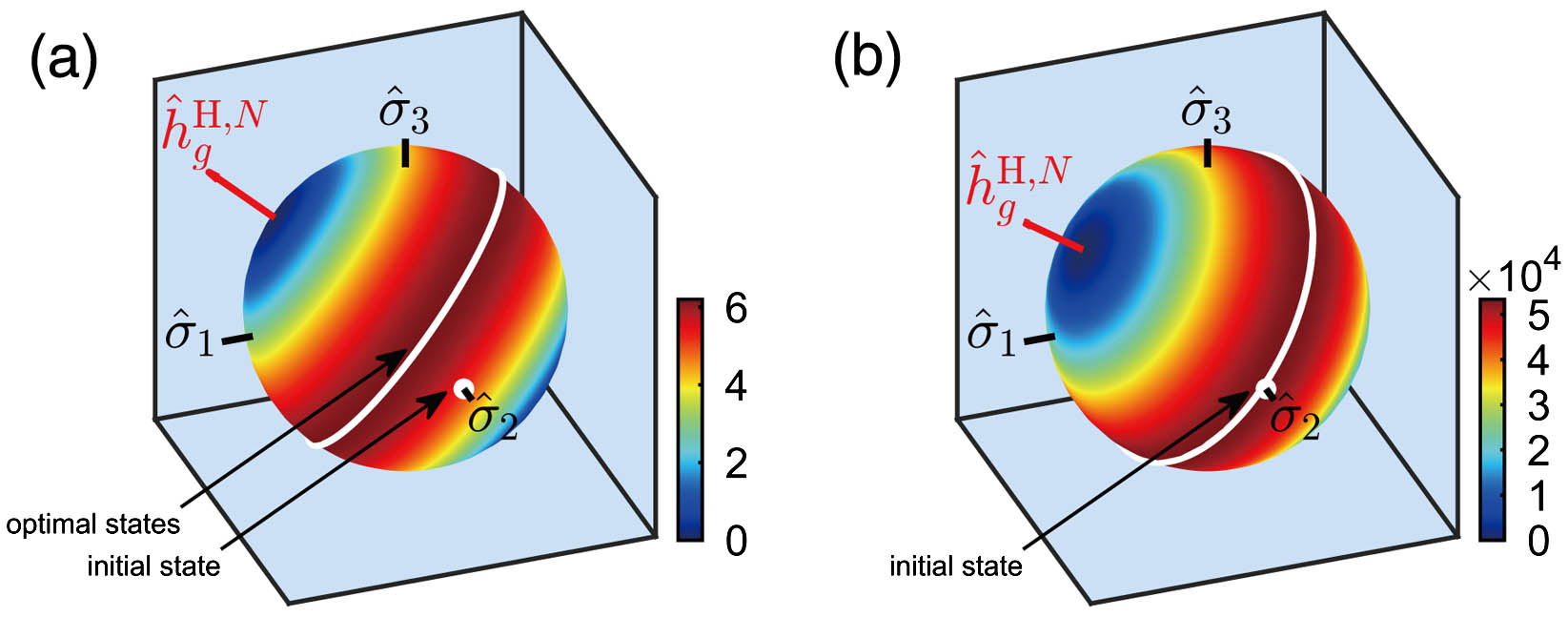
Quantum parameter estimation is a crucial tool for inferring unknown parameters in physical models from experimental data. The Jaynes–Cummings model is a widely used model in quantum optics that describes the interaction between an atom and a single-mode quantum optical field. In this Letter, we systematically investigate the problem of estimating the atom-light coupling strength in this model and optimize the initial state in the full Hilbert space. We compare the precision limits achievable for different optical field quantum states, including coherent states, amplitude- and phase-squeezed states, and provide experimental suggestions with an easily prepared substitute for the optimal state. Our results provide valuable insights into optimizing quantum parameter estimation in the Jaynes–Cummings model and can have practical implications for quantum metrology with hybrid quantum systems.
quantum Fisher information Jaynes–Cummings model parameter estimation theory Chinese Optics Letters
2023, 21(10): 102701
1 同济大学土木工程学院建筑工程系,上海 200092
2 同济大学工程结构性能演化与控制教育部重点试验室,上海 200092
3 苏州热工研究院有限公司,江苏 苏州 215004
长期辐射环境作用下,混凝土力学性能会发生退化影响堆坑混凝土结构乃至核电站的长寿期运行。以核辐射环境下混凝土及其组分的体积和力学性能的多尺度演化为主线,回顾分析相关研究成果。现有研究对核辐射诱导矿物组分、骨料、硬化水泥浆及混凝土的体积变化和力学性能演化机理和规律有了基本的认识,建立了混凝土体积膨胀和力学性能多尺度演化的基本数值模型。为可靠预测辐照混凝土力学性能,需要充分关注骨料的随机分布和不同组分的辐照效应差异,建立基于矿物组成的辐照混凝土力学性能退化的多尺度模型。
混凝土 中子辐射 γ辐射 体积膨胀 性能退化 多尺度模型 concrete neutron radiation γ radiation swelling performance degradation multi-scale model

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 State Key Laboratory of Precision Spectroscopy, Department of Physics, School of Physics and Electronic Science, East China Normal University, Shanghai 200062, China
2 Shanghai Branch, Hefei National Laboratory, Shanghai 201315, China
3 School of Physics and Astronomy, and Tsung-Dao Lee Institute, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai 200240, China
4 Shanghai Research Center for Quantum Sciences, Shanghai 201315, China
5 Collaborative Innovation Center of Extreme Optics, Shanxi University, Taiyuan 030006, China
Photon number-squeezed states are of significant value in fundamental quantum research and have a wide range of applications in quantum metrology. Most of their preparation mechanisms require precise control of quantum dynamics and are less tolerant to dissipation. We propose a mechanism that is not subject to these restraints. In contrast to common approaches, we exploit the self-balancing between two types of dissipation induced by positive- and negative-temperature reservoirs to generate steady states with sub-Poissonian statistical distributions of photon numbers. We also show how to implement this mechanism with cavity optomechanical systems. The quality of the prepared photon number-squeezed state is estimated by our theoretical model combined with realistic parameters for various typical optomechanical systems.
Photonics Research
2023, 11(9): A26
1 微米纳米加工技术全国重点实验室, 上海 200241
2 上海交通大学 微纳电子学系, 上海 200241
近年来仿生扑翼飞行器利用视觉系统自主飞行成为一个具有广泛前景的研究方向, 然而, 其有限的带载能力对视觉传感器的类型、尺寸和重量提出了严格要求。目前商用图像处理模块的尺寸和重量较大, 且需要回传图像信息至地面控制系统处理, 文章旨在设计一款轻量化机载单目视觉系统, 帮助微型仿生扑翼飞行器获取外界信息并实现智能自主的飞行。相比于其他图像处理模块, 此系统以国产高算力芯片K210为核心进行设计, 可脱离电脑端完成图像处理, 尺寸仅为2.2cm×2.3cm, 重量仅为3g, 内部兼容轻量化网络模型实现分类识别, 通过串口进行信息交互, 控制扑翼飞行器实现手势识别和目标追踪。
仿生飞行器 单目视觉系统 卷积神经网络 轻量化 目标识别 机载图像处理 串口通信 自主飞行 bionic aircraft monocular vision system convolution neural network lightweight target recognition onboard image processing serial communication autonomous flight
1 微米纳米加工技术国家级重点实验室, 上海 200240
2 上海交通大学 电子信息与电气工程学院 微纳电子学系, 上海 200240
提出并研制了一种具有高机械灵敏度和低零偏稳定性的新型波浪式MEMS谐振陀螺(WDRG)。该结构的设计方法是将传统的环式MEMS谐振陀螺(DRG)转变为波浪式环, 以提供更高的热弹性品质因数。此外, 与传统DRG相比, WDRG具有更高的制造误差抗扰度。通过优化结构参数, 进一步提高了WDRG的性能。通过有限元法(FEM)给出了主要结构参数对WDRG性能的影响。优化后WDRG的热弹性品质因数、机械灵敏度和偏置稳定性分别为450k, 1.05μm/(°/s)和0.076(°)/h。与传统DRG相比, 零偏稳定性降低了90%, 热弹性品质因数和机械灵敏度分别提高了215%和950%。
1 上海交通大学 微米/纳米加工技术国家级重点实验室
2 电子信息与电气工程学院 微纳电子学系, 上海 200240
3 上海交通大学 微米/纳米加工技术国家级重点实验室
微谐振陀螺仪是一种固体波动陀螺, 常采用微纳制造工艺进行加工, 具有小体积、高性能、低功耗、批量化等特点。自1975年世界上第一个半球谐振陀螺诞生以来, 微谐振陀螺的谐振子拓扑结构经历了三维结构到二维结构的演变。文章以拓扑结构的发展脉络为主线, 对微谐振陀螺的发展过程进行了梳理和总结, 最后对目前存在的问题进行了分析, 对未来的发展进行了展望。

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 State Key Laboratory of Precision Spectroscopy, School of Physics and Electronic Science, East China Normal University, Shanghai 200062, China
2 Shanghai Research Center for Quantum Sciences, Shanghai 201315, China
3 School of Physics and Astronomy, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, and Tsung-Dao Lee Institute, Shanghai 200240, China
4 Collaborative Innovation Center of Extreme Optics, Shanxi University, Taiyuan 030006, China
5 e-mail: chyuan@phy.ecnu.edu.cn
6 e-mail: wpzhang@phy.ecnu.edu.cn
The accelerometer plays a crucial role in inertial navigation. The performance of conventional accelerometers such as lasers is usually limited by the sensing elements and shot noise limitation (SNL). Here, we propose an advanced development of an accelerometer based on atom–light quantum correlation, which is composed of a cold atomic ensemble, light beams, and an atomic vapor cell. The cold atomic ensemble, prepared in a magneto-optical trap and free-falling in a vacuum chamber, interacts with light beams to generate atom–light quantum correlation. The atomic vapor cell is used as both a memory element storing the correlated photons emitted from cold atoms and a bandwidth controller through the control of free evolution time. Instead of using a conventional sensing element, the proposed accelerometer employs interference between quantum-correlated atoms and light to measure acceleration. Sensitivity below SNL can be achieved due to atom–light quantum correlation, even in the presence of optical loss and atomic decoherence. Sensitivity can be achieved at the level, based on evaluation via practical experimental conditions. The present design has a number of significant advantages over conventional accelerometers such as SNL-broken sensitivity, broad bandwidth from a few hundred Hz to near MHz, and avoidance of the technical restrictions of conventional sensing elements.
Photonics Research
2022, 10(4): 04001022

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 State Key Laboratory of Precision Spectroscopy, Quantum Institute for Light and Atoms, Department of Physics, East China Normal University, Shanghai 200062, China
2 School of Physics and Astronomy, and Tsung-Dao Lee Institute, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai 200240, China
3 Shanghai Research Center for Quantum Sciences, Shanghai 201315, China
4 Collaborative Innovation Center of Extreme Optics, Shanxi University, Taiyuan 030006, China
5 e-mail: lqchen@phy.ecnu.edu.cn
Quantum non-demolition (QND) measurement is an important tool in the fields of quantum information processing and quantum optics. The atom-light hybrid interferometer is of great interest due to its combination of an atomic spin wave and an optical wave, which can be utilized for photon number QND measurement via the AC-Stark effect. In this paper, we present an SU(1,1)-SU(2)-concatenated atom-light hybrid interferometer, and theoretically study QND measurement of the photon number. Compared to the traditional SU(2) interferometer, the signal-to-noise ratio in a balanced case is improved by a gain factor of the nonlinear Raman process (NRP) in this proposed interferometer. Furthermore, the condition of high-quality QND measurement is analyzed. In the presence of losses, the measurement quality is reduced. We can adjust the gain parameter of the NRP in the readout stage to reduce the impact due to losses. Moreover, this scheme is a multiarm interferometer, which has the potential of multiparameter estimation with many important applications in the detection of vector fields, quantum imaging, and so on.
Photonics Research
2022, 10(2): 02000475
1 上海交通大学 微米纳米加工技术国家级重点实验室, 上海 200240
2 上海交通大学 电子信息与电气工程学院微纳电子学系, 上海200240
为了探测月面静海熔岩管道区域, 该文设计了一套微型折叠探测机器人控制系统。采用MPU6050姿态传感器、光照传感器、红外传感器等构建机器人感知系统, 使用NRF24L01远距离通信电路和图像传输接收机构建机器人数据通信链路, 使用基于Qt的C++编程设计微型探测机器人控制系统上位机实现微型折叠探测机器人的运行。测试结果表明, 微型折叠探测机器人运行速度可达0.5 m/s, 爬坡角度为20.0°, 折叠角度为47.3°, 通信距离为200.0 m, 质量仅204.1 g。
探测机器人 上位机 比例、积分、微分(PID) detection robot NRF24L01 NRF24L01 STM32 STM32 host computer proportion、integral、differential(PID)
1 上海交通大学 1. 微米/纳米加工技术国家级重点实验室
2 2. 电子信息与电气工程学院 微纳电子学系, 上海 200240
为了满足微型无人飞行器实时控制的要求, 文章对Yolo-V4单阶段图像检测算法进行了轻量化设计, 并基于单目摄像头设计了实时目标识别系统。该轻量化算法首先通过优化输入网络的分辨率和卷积层参数等方法, 将主干网络由73层压缩到16层; 然后通过简化残差结构和跨级结构, 解决深层网络梯度消失问题, 减少梯度信息重复; 最后自下而上将网络浅层和深层特征进行了精简融合。采用K均值聚类算法训练轻量化模型以优化预选框参数, 提高算法对特定目标的检测精度。测试表明, 改进后的轻量化算法对特定目标的预测精度为98%, 召回率为92%, 均值平均精度达90.70%, 单张图片检测时间为7.8ms, 对视频的处理速度可达125.6f/s, 满足微型无人飞行器的实时应用要求。
实时目标识别 深度学习 轻量化 单目视觉 YoloV4 YoloV4 real-time target recognition deep learning lightweight monocular vision





